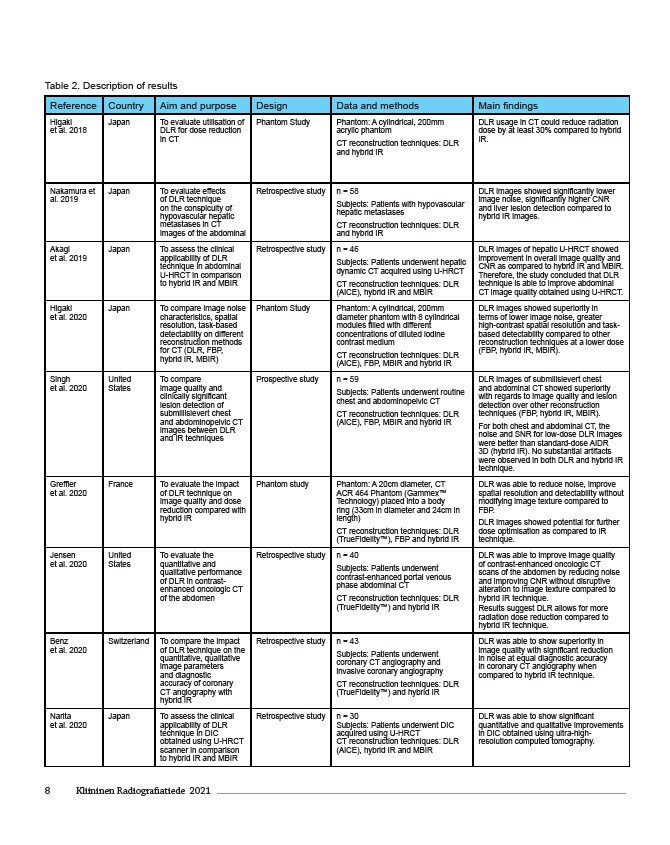
Reference Country Aim and purpose Design Data and methods Main findings
Higaki
Japan To evaluate utilisation of
et al. 2018
DLR for dose reduction
in CT
8 Kliininen Radiografiatiede 2021
Phantom Study Phantom: A cylindrical, 200mm
acrylic phantom
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
and hybrid IR
DLR usage in CT could reduce radiation
dose by at least 30% compared to hybrid
IR.
Nakamura et
al. 2019
Japan To evaluate effects
of DLR technique
on the conspicuity of
hypovascular hepatic
metastases in CT
images of the abdominal
Retrospective study n = 58
Subjects: Patients with hypovascular
hepatic metastases
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
and hybrid IR
DLR images showed significantly lower
image noise, significantly higher CNR
and liver lesion detection compared to
hybrid IR images.
Akagi
et al. 2019
Japan To assess the clinical
applicability of DLR
technique in abdominal
U-HRCT in comparison
to hybrid IR and MBIR
Retrospective study n = 46
Subjects: Patients underwent hepatic
dynamic CT acquired using U-HRCT
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
(AiCE), hybrid IR and MBIR
DLR images of hepatic U-HRCT showed
improvement in overall image quality and
CNR as compared to hybrid IR and MBIR.
Therefore, the study concluded that DLR
technique is able to improve abdominal
CT image quality obtained using U-HRCT.
Higaki
et al. 2020
Japan To compare image noise
characteristics, spatial
resolution, task-based
detectability on different
reconstruction methods
for CT (DLR, FBP,
hybrid IR, MBIR)
Phantom Study Phantom: A cylindrical, 200mm
diameter phantom with 8 cylindrical
modules filled with different
concentrations of diluted iodine
contrast medium
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
(AiCE), FBP, MBIR and hybrid IR
DLR images showed superiority in
terms of lower image noise, greater
high-contrast spatial resolution and task-based
detectability compared to other
reconstruction techniques at a lower dose
(FBP, hybrid IR, MBIR).
Singh
et al. 2020
United
States
To compare
image quality and
clinically significant
lesion detection of
submillisievert chest
and abdominopelvic CT
images between DLR
and IR techniques
Prospective study n = 59
Subjects: Patients underwent routine
chest and abdominopelvic CT
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
(AiCE), FBP, MBIR and hybrid IR
DLR images of submilisievert chest
and abdominal CT showed superiority
with regards to image quality and lesion
detection over other reconstruction
techniques (FBP, hybrid IR, MBIR).
For both chest and abdominal CT, the
noise and SNR for low-dose DLR images
were better than standard-dose AIDR
3D (hybrid IR). No substantial artifacts
were observed in both DLR and hybrid IR
technique.
Greffier
et al. 2020
France To evaluate the impact
of DLR technique on
image quality and dose
reduction compared with
hybrid IR
Phantom study Phantom: A 20cm diameter, CT
ACR 464 Phantom (Gammex™
Technology) placed into a body
ring (33cm in diameter and 24cm in
length)
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
(TrueFidelity™), FBP and hybrid IR
DLR was able to reduce noise, improve
spatial resolution and detectability without
modifying image texture compared to
FBP.
DLR images showed potential for further
dose optimisation as compared to IR
technique.
Jensen
et al. 2020
United
States
To evaluate the
quantitative and
qualitative performance
of DLR in contrast-enhanced
oncologic CT
of the abdomen
Retrospective study n = 40
Subjects: Patients underwent
contrast-enhanced portal venous
phase abdominal CT
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
(TrueFidelity™) and hybrid IR
DLR was able to improve image quality
of contrast-enhanced oncologic CT
scans of the abdomen by reducing noise
and improving CNR without disruptive
alteration to image texture compared to
hybrid IR technique.
Results suggest DLR allows for more
radiation dose reduction compared to
hybrid IR technique.
Benz
et al. 2020
Switzerland To compare the impact
of DLR technique on the
quantitative, qualitative
image parameters
and diagnostic
accuracy of coronary
CT angiography with
hybrid IR
Retrospective study n = 43
Subjects: Patients underwent
coronary CT angiography and
invasive coronary angiography
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
(TrueFidelity™) and hybrid IR
DLR was able to show superiority in
image quality with significant reduction
in noise at equal diagnostic accuracy
in coronary CT angiography when
compared to hybrid IR technique.
Narita
et al. 2020
Japan To assess the clinical
applicability of DLR
technique in DIC
obtained using U-HRCT
scanner in comparison
to hybrid IR and MBIR
Retrospective study n = 30
Subjects: Patients underwent DIC
acquired using U-HRCT
CT reconstruction techniques: DLR
(AiCE), hybrid IR and MBIR
DLR was able to show significant
quantitative and qualitative improvements
in DIC obtained using ultra-high-resolution
computed tomography.
Table 2. Description of results