SpringerLink. The electronic databases
selected were comprehensive, and con-tains
peer reviewed full-text literature
that could potentially answer the re-search
questions. Searches were done
in the beginning of May 2020 and were
limited to articles written in English and
published between April 2016 and April
2020. A five year limit was set due to the
novelty of DLR technique. The authors
queried the four databases systematical-ly
using a combination of keywords and
controlled vocabulary terms as detailed
in Table 1. The selection process is also
illustrated on the PRISMA diagram as
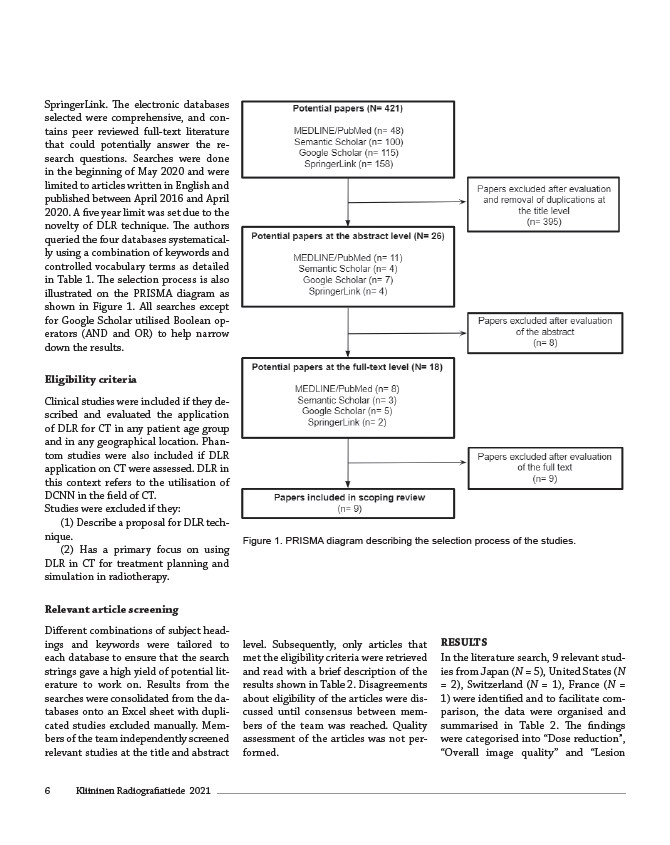
shown in Figure 1. All searches except
for Google Scholar utilised Boolean op-erators
(AND and OR) to help narrow
down the results.
Eligibility criteria
Clinical studies were included if they de-scribed
and evaluated the application
of DLR for CT in any patient age group
and in any geographical location. Phan-tom
studies were also included if DLR
application on CT were assessed. DLR in
this context refers to the utilisation of
DCNN in the field of CT.
Studies were excluded if they:
(1) Describe a proposal for DLR tech-nique.
(2) Has a primary focus on using
DLR in CT for treatment planning and
simulation in radiotherapy.
Relevant article screening
Different combinations of subject head-ings
and keywords were tailored to
each database to ensure that the search
strings gave a high yield of potential lit-erature
to work on. Results from the
searches were consolidated from the da-tabases
onto an Excel sheet with dupli-cated
studies excluded manually. Mem-bers
of the team independently screened
relevant studies at the title and abstract
6 Kliininen Radiografiatiede 2021
Figure 1. PRISMA diagram describing the selection process of the studies.
level. Subsequently, only articles that
met the eligibility criteria were retrieved
and read with a brief description of the
results shown in Table 2. Disagreements
about eligibility of the articles were dis-cussed
until consensus between mem-bers
of the team was reached. Quality
assessment of the articles was not per-formed.
RESULTS
In the literature search, 9 relevant stud-ies
from Japan (N = 5), United States (N
= 2), Switzerland (N = 1), France (N =
1) were identified and to facilitate com-parison,
the data were organised and
summarised in Table 2. The findings
were categorised into “Dose reduction”,
“Overall image quality” and “Lesion